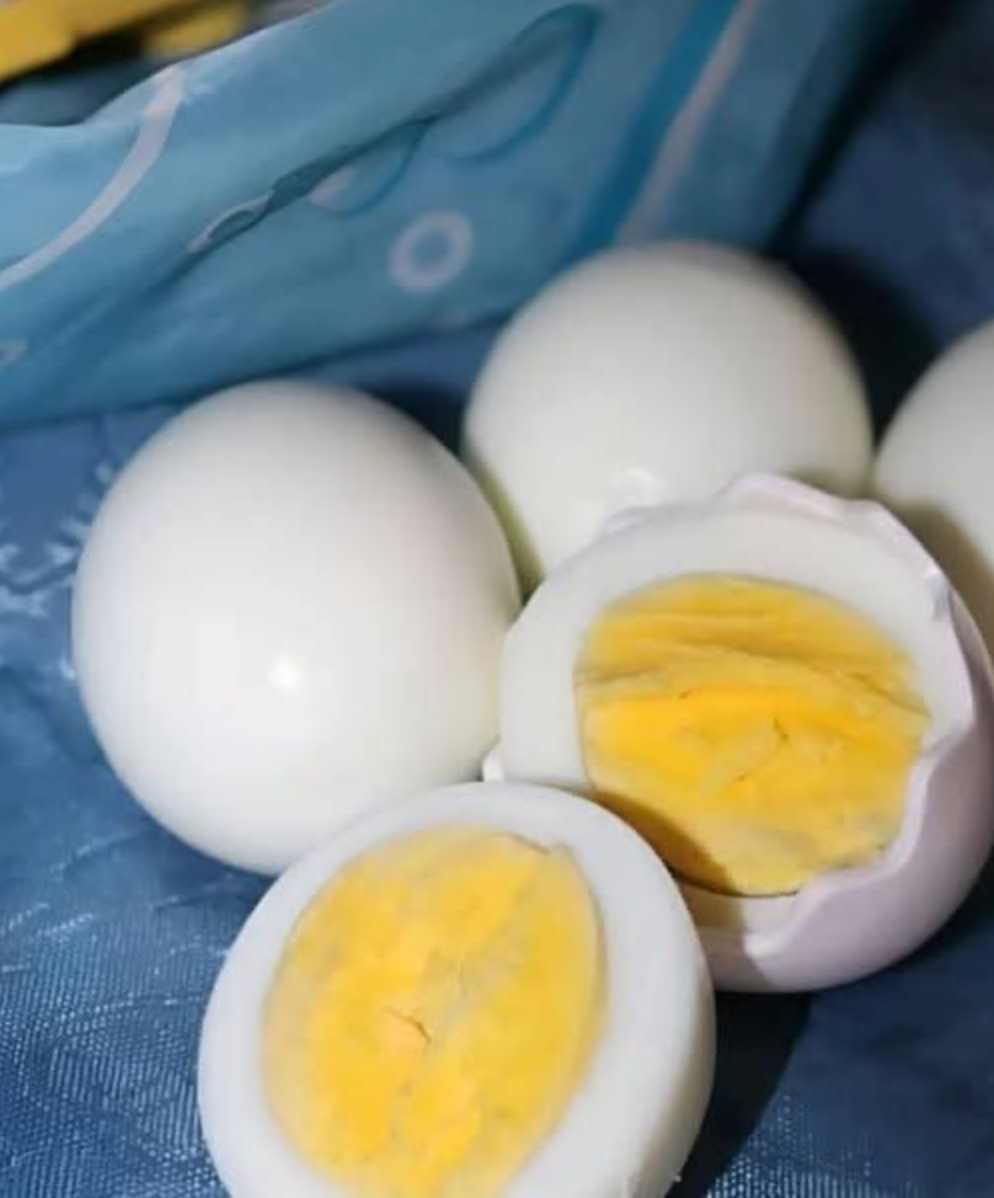
Eggs are one of the most versatile and nutrient-dense foods you can eat. Whether you enjoy them boiled, fried, scrambled, or poached, eggs provide high-quality protein, essential vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats. However, when it comes to choosing the healthiest breakfast option, the way eggs are cooked can make a significant difference. Let’s explore the differences between boiled eggs and fried eggs, including nutrition, health impacts, and tips for incorporating them into a balanced diet.
Nutritional Profile of Eggs
Eggs are often called a superfood because they pack a variety of nutrients into a small package:
- Protein: About 6–7 grams per egg, containing all nine essential amino acids
- Healthy fats: Primarily unsaturated fats, with around 5 grams per egg
- Vitamins: Rich in vitamin B12, riboflavin, and vitamin D
- Minerals: Selenium, phosphorus, and choline for brain health
- Antioxidants: Lutein and zeaxanthin for eye health
Cooking method can influence the calorie content, fat composition, and digestibility of these nutrients.
Boiled Eggs
How They’re Made:
Boiled eggs are cooked in their shells in water, either until the yolk is soft (soft-boiled) or fully set (hard-boiled). No added fat is needed.
Health Advantages:
- Lower in calories: Because no oil or butter is used, boiled eggs have fewer calories than fried eggs.
- Heart-friendly: Boiling preserves the egg’s natural fat without adding extra saturated fats.
- Stable nutrients: Vitamins like B12 and minerals like selenium remain intact during boiling.
- Convenient for meal prep: Boiled eggs can be stored in the fridge for several days, making them a great grab-and-go option.
Potential Downsides:
- Boiled eggs may feel less flavorful to some people because they lack the added fats and browning that frying provides.
- Overcooking hard-boiled eggs can cause a slightly green ring around the yolk, which is harmless but affects aesthetics.
Fried Eggs
How They’re Made:
Fried eggs are cooked in a pan with oil, butter, or other fats. They can be prepared sunny-side-up, over-easy, or over-hard, depending on preference.
Health Advantages:
- Enhanced flavor: Frying adds richness and a crispy texture, making eggs more satisfying for some.
- Fat-soluble nutrient absorption: Certain vitamins (A, D, E, K) are better absorbed when eaten with some fat, so frying in a small amount of healthy oil can aid absorption.
- Versatility: Frying allows pairing with vegetables, lean proteins, or whole grains for a nutrient-packed breakfast.
Potential Downsides:
- Higher in calories: The addition of oil or butter can add 40–100+ calories per egg, depending on the type and amount used.
- Potential for harmful compounds: High-heat frying can produce oxidized cholesterol and advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), which may contribute to inflammation if consumed excessively.
- Increased saturated fat: Using butter or certain oils can raise saturated fat intake, which may impact heart health if eaten frequently.
Comparative Summary
| Feature | Boiled Eggs | Fried Eggs |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | Lower (approx. 70 cal/egg) | Higher (approx. 90–150 cal/egg, depending on oil/butter) |
| Fat Content | 5 g (naturally occurring) | 7–12 g (depends on cooking fat) |
| Protein | 6–7 g | 6–7 g |
| Nutrient Preservation | Excellent | Good (some antioxidants may degrade at high heat) |
| Heart Health | Better option due to no added fat | Moderate; depends on cooking fat choice |
| Convenience | Easy to prepare ahead | Needs immediate cooking; may require cleaning pan |
| Flavor & Texture | Mild, neutral | Rich, savory, crispy edges |
Tips for Making Fried Eggs Healthier
If you prefer fried eggs but want to keep them nutritious:
- Use healthy oils: Opt for olive oil, avocado oil, or a small amount of coconut oil instead of butter.
- Control heat: Cook over medium heat to prevent burning and reduce formation of harmful compounds.
- Pair with veggies: Add spinach, tomatoes, or mushrooms to increase fiber and antioxidants.
- Limit extra fats: Skip excessive cheese or processed meats to maintain balance.
The Bottom Line
- Boiled eggs are generally considered the healthiest breakfast choice if your priority is lower calorie intake, heart health, and convenience.
- Fried eggs can still be part of a healthy diet, especially when cooked with healthy oils and paired with nutrient-dense foods, but they come with slightly higher calorie and fat content.
- Both boiled and fried eggs provide high-quality protein and essential nutrients, so the “best” choice depends on your dietary goals, taste preference, and overall lifestyle.
Pro tip: Mixing your breakfast methods—boiling some eggs for grab-and-go protein and occasionally frying eggs for a richer, more satisfying meal—can give you the best of both worlds.